Understanding Exempt Research vs Not HSR
Introduction
Investigators often encounter confusion between research that is exempt under federal regulations and activities that are not human subjects research (NHSR). Exempt research refers to studies that involve human subjects but fall into specific categories outlined in the Common Rule (45 CFR 46.104). In contrast, NHSR activities do not meet the definition of human subjects research, typically because they do not involve living individuals or identifiable private information. Understanding this distinction is critical for determining whether IRB review is required and what level of oversight applies. This guidance provides clarity on these terms and the IRB review process.
Terms
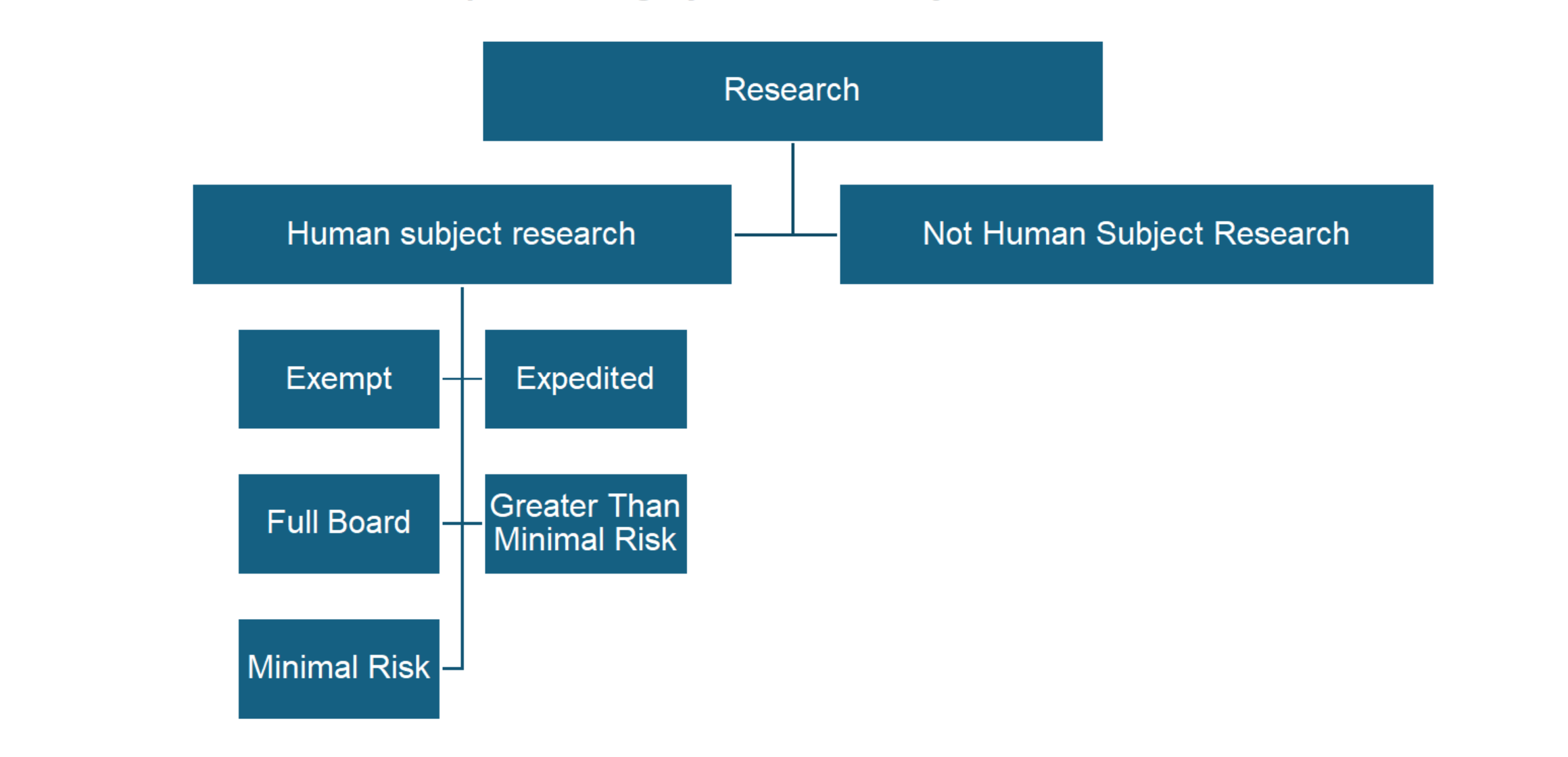
- Human Subjects Research (HSR): A project that meets BOTH definitions of “research” and “human subjects”.
- Research: A systematic investigation, including research development, testing and evaluation, designed to develop or contribute to generalizable knowledge. Activities that meet this definition constitute research even if they are a component of another non-research activity (e.g., instruction, community service, program evaluation, quality improvement, demonstration).
- Human Subject: A living individual about whom an investigator (whether professional or student) conducting research obtains:
- a) data through intervention or interaction with the individual, or
- b) identifiable private information, even if no intervention or interaction with the researcher occurs.
- Exempt Research:
- A subset of human subjects research that involves no more than minimal risk and fits into one or more Exemption categories under federal regulation 45 CFR 46.104.
“Exempt” does not mean the research is free from oversight or ethical responsibilities. It simply indicates that the study is relieved from certain regulatory requirements, but not all. Because the activity still qualifies as human subjects research, appropriate protections for participants must be in place.
-
- Example of research activities that might meet an Exempt category:
- Educational practices in established settings
- Surveys, interviews, or observation of public behavior (with privacy safeguards)
- Benign behavioral interventions in adults
- Secondary research using publicly available or de-identified data
- Taste and food quality evaluations
- Example of research activities that might meet an Exempt category:
- Not Human Subjects Research (NHSR):
- Activities that do not meet the definition of human subjects research.
- Examples:
- Studies on deceased individuals
- Public health surveillance activities authorized by a public health authority
- Scholarly/journalistic activities (e.g., oral history, biography)
Exempt is a category of Human Subject Research
What is Generalizable Knowledge?
Generalizable knowledge is knowledge that:
- Extends beyond the study population and can be applied to other people, settings, or circumstances.
- Is designed to develop or contribute to a broader understanding of a phenomenon, theory, or principle.
- Is typically disseminated through publication, presentations, or sharing with the scientific community.
Key Characteristics
- Not just for internal use: If the data is collected solely for internal decision-making (e.g., program evaluation within an organization), it usually does not qualify as generalizable knowledge.
- Research intent matters: If the purpose is to draw conclusions that others can use or replicate, it is considered generalizable.
How to Request a Determination from the IRB
When you are unsure whether your project qualifies as Not Human Subjects Research or requires a submission to the IRB, you may email the Office of Regulatory Services at regulatoryservices@uta.edu.
In the email include:
- Project Summary: Include research objectives, methodology, and data sources.
- Data Details: Specify whether data involves living individuals, identifiable information, or public datasets.
Refer to the IRB’s definitions to ensure you are using terms accurately in your project summary, especially commonly misunderstood terms like ‘de-identified’ or ‘coded’ data.
The IRB staff will review and advise on whether the activity is not human subjects research. If the activity is human subjects research, a protocol application must be submitted in Mentis for IRB review and approval.
